How to Grow Cannabis Hydroponically

Article written by

Homegrown Cannabis Co.American Seed Bank and Cultivation Experts
Content reviewed by

Dr. Lewis JasseyMedical Director - Pediatric Medicine
Hydroponic growing is a method of cultivating cannabis plants in a solution of water and nutrients. The system is tightly controlled, simple to set up, and has immense harvest-boosting potential.
How does a basic hydro system look, and how do you use it? Here’s how to grow weed in water!
Get Your Medical Card
Connect with a licensed physician online in minutes.
What Is Hydroponic Growing?
Hydroponic farming is one of the three most popular grow systems for marijuana. Astronauts have also used it to cultivate leafy greens like lettuce in outer space. It relies on water-based mineral solutions instead of soil to house, support, and feed the roots.
At its simplest, this set-up consists of a reservoir with water and a tray with potted marijuana.
You fill plant containers with an inert substrate, like coco or Rockwool, and germinate seeds. The reservoir holds fertilizer-rich water to feed your weed.
Pots sit in a tray above the reservoir, and roots push down into the water. They absorb all minerals required to survive and thrive when they touch the liquid.
Types of Hydroponic Cannabis Growing
Hydroponic gardens may be active or passive, depending on their use of electronic devices.
Active
Active systems use air stones to aerate the water and electric pumps to move the nutrient solution. Since they utilize technology, you can automate them to reduce your workload.
Passive
Passive systems are inexpensive, minimalist, and low-tech. In this version, string or cloth wicks hang above the reservoir, soak in, and transport nutrient-rich water to plant roots.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Here’s why you’d pick or skip a hydroponic growing system for cultivating cannabis indoors.
Advantages
Weed gardeners love hydro because it gives them outstanding control over feeding. Here are some additional advantages:
- Faster growth and higher yields: Hydroponic plants exhibit prolific vegetative development due to greater nutrient availability.
- Lower risk of pests: Most problematic insects require soil to survive and don’t attack hydro-grown roots, stems, foliage, and buds.
- Greater water efficiency: Water re-circulates instead of draining in most hydroponic setups, reducing usage.
Disadvantages
Here are the challenges you may face with hydroponic growing:
- Technical complexity: Your plant nutrition is under your exclusive control. You must pay more attention to avoid nutrient deficiencies and burns. The more plants you grow, the more complex it is regarding how much feed you need.
- Extra equipment: Besides accurate EC and pH meters, you need a tank to set up hydro. Some systems also require water pumps and air stones.
- Higher risk of plant disease: Soil microbes buffer the roots against illnesses, while hydro leaves them open to attacks.
What You’ll Need to Get Started
Hydroponic growing is somewhat pricier than traditional gardening, but it doesn’t have to be exorbitant. Basic setups can cost under $250 and produce excellent results.
Growing Media
The growing medium is a firm substance that anchors the intersection of crop stem and roots. Cultivators can choose clay pebbles, peat moss, Rockwool cubes, or coco coir.
Water and Nutrients
Distilled or tap water with reverse osmosis filtration is optimal for hydroponic systems. Don’t forget to treat it with appropriate amounts of hydro-specific fertilizer for the growth stage.
Light Source
Choose HPS or LED grow lights and hang them at a suitable distance above the canopy.
Best Strains for Hydroponic Cannabis
Given proper care, any cultivar can thrive without soil. If you’re a beginner, choosing the top hydro strains (e.g., Sour Diesel, Blue Dream, Northern Lights) can increase your success rate. These types of marijuana are compact, resistant to nutrient fluctuations, and thrive in controlled environments.
Setup
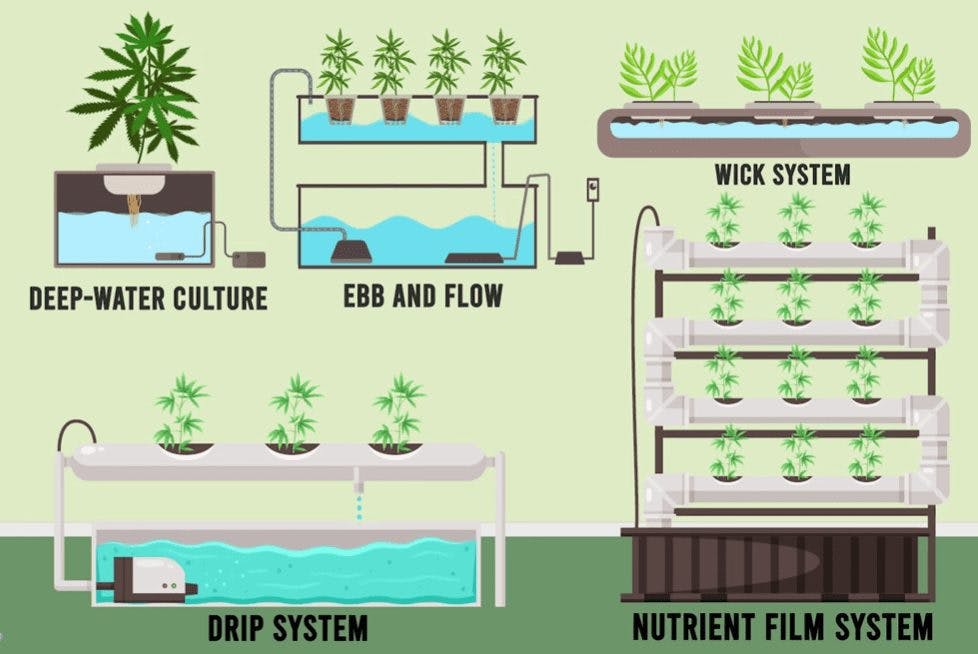
Growers can choose among these five hydroponic setups.
Drip System
The drip system consists of a large tray connected to pipes and an external tank with a submersible pump and air stones. It continuously sends small doses of food and water to plants. Roots sit in the open air, and drained liquids return to the water reservoir.
Wick System
The wick system has holes in the medium, eliminating the need for an air pump to introduce oxygen. It features a container and a separate tank with a nutrient solution. Wicks are in between, passively transporting nutrients to roots through capillary action.
Ebb and Flow
Ebb and flow (aka flood and drain) systems consist of buckets suspended above a growing tray with a water inlet and outlet. Instead of non-stop submerging the root system, a pump periodically floods the bucket and feeds the plants.
Nutrient Film System
The nutrient film technique is similar to ebb and flow but constantly streams water to the roots through pumps. The tray sits at an angle, so excess liquid streams back down after passing the root zone.
Deep Water Culture
Deep water culture systems use a single reservoir filled with an aerated nutrient solution. Crops sit in cups slotted into a Styrofoam sheet on the surface while roots float underneath. Air stones produce oxygen bubbles, letting them breathe.
The passive version of DWC is called the Kratky system. It uses the same principle but adds a layer of open air between water and roots.
Must-Follow Tips for a Successful Hydroponic Grow
Hydroponic gardeners see the best results when they:
- Test hydroponic growing media, water, and nutrients regularly. Cannabis absorbs food best in slightly acidic environments, thriving at 5.5–6.0 pH levels.
- Keep the water temperature at around 70°F. Employ heaters and chillers to maintain an optimal environment.
- Clean the reservoir regularly to eliminate invading pathogens and water-borne diseases.
- Keep plant nutrition in check by purchasing hydro fertilizer with essential nutrients for vegging and flowering crops.
The Bottom Line
Hydroponic gardening may seem overly complicated to an outside observer, but it’s not a complex subject. The key is to start simple and stay on top of your strain’s environmental requirements. Do so, and the cultivation journey will be straightforward and very rewarding.
This alternative to soil cultivation is ideal for intermediate and advanced growers looking to step up their game. Even newbies can master it through prep work and research, though. If this level of control over your setup sounds appealing, there’s no reason to skip it.
Get Your Medical Card
Connect with a licensed physician online in minutes.
