HHC vs. THC: What’s the Difference?

Article written by

Dipak HemrajHead of Research and Education
Content reviewed by

Dr. Lewis JasseyMedical Director - Pediatric Medicine
Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) are both cannabinoids found within cannabis products. HHC is one of the newer cannabinoids on the market, and further research into the compound is needed to determine the legitimacy of its benefits.
However, some anecdotal evidence suggests that the main difference between HHC and THC is HHC’s overall stability. In other words, it has a longer shelf life than THC.
Get your medical marijuana card
Connect with a licensed physician online in minutes.
What Is HHC?
Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) is a naturally occurring phytocannabinoid found in the cannabis plant and is considered a minor cannabinoid. HHC is a hydrogenated derivative of delta-8 and delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
Although HHC is naturally found in Cannabis sativa in small amounts, it can be produced synthetically by hydrogenation (adding molecular hydrogen to a double bond) of cannabis extracts. The hydrogenation process was first used to convert THC to HHC in 1944 when a chemist named Roger Adams added hydrogen atoms to the compound delta-9 THC.
HHC can also be made from cannabidiol (CBD).
Although there is not a lot of research or data on HHC, people have reported that it has euphoric effects similar to THC, making it a psychoactive cannabinoid. Due to its similarity to THC, HHC may have anti-inflammatory, anti-emetic (anti-nausea and vomiting), and appetite-stimulating properties, making it potentially very useful for managing chronic pain, insomnia, and the side effects of chemotherapy.
The Chemistry Behind HHC
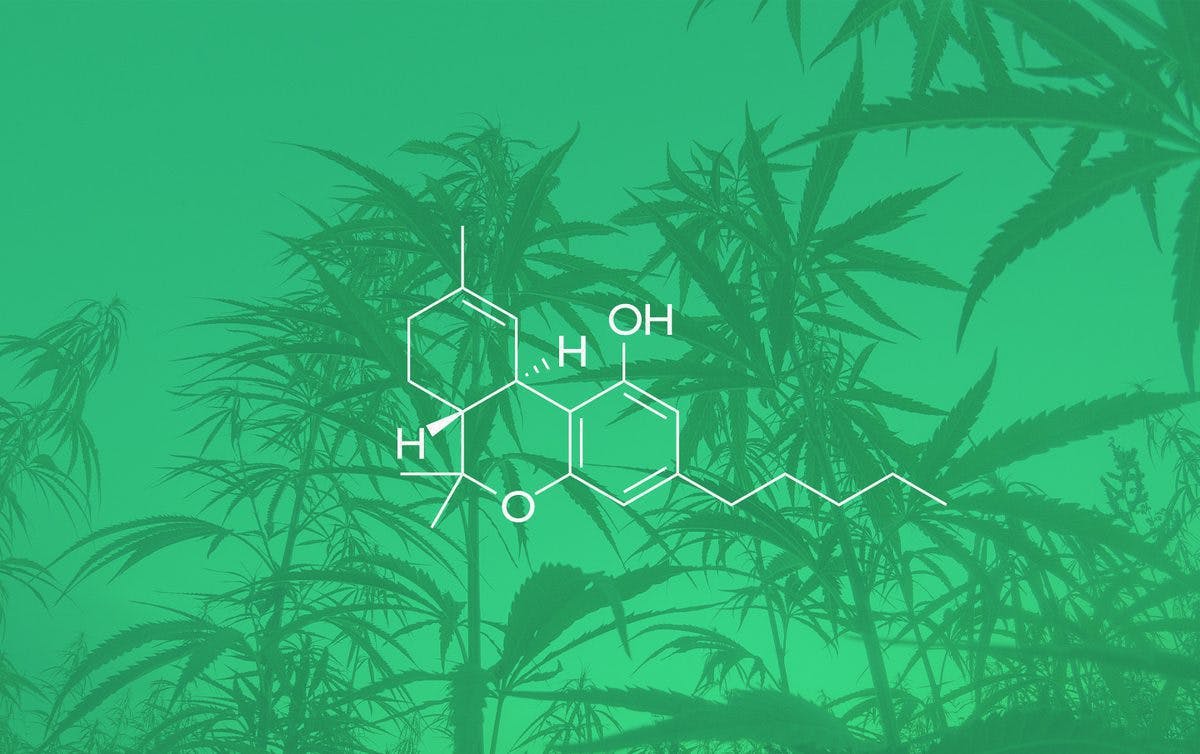
HHC is a cannabinoid in cannabis that, like cannabinol (CBN), is a degradation byproduct of THC. HHC can also be produced by hydrogenation of cannabis extracts, meaning that two hydrogen atoms (H2) are added to THC. The molecular formula for HHC is C21H32O2, whereas THC’s is C21H30O2.
Unlike delta-8 and delta-9 THC, HHC has no double bonds in the cyclohexyl ring. HHC is also structurally similar to the novel cannabis constituent cannabiripsol.
Hexahydrocannabinol should not be confused with the related compounds 9-Nor-9β-hydroxy-hexahydro cannabinol (9-Nor-9Beta-HHC), 9-Hydroxyhexahydrocannabinol (9-OH-HHC), or 11-Hydroxyhexahydrocannabinol (11-OH-HHC and 7-OH-HHC).
How It Works
HHC binds to cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) but with weaker affinity than THC. Therefore, it produces intoxicating and psychoactive effects, but much less than THC.
That’s because adding hydrogen molecules to delta-9 THC decreases the ability of HHC to bind to CB1 and CB2 receptors within the body’s endocannabinoid system, as well as specific pain receptors in the body.
This hydrogenated form also increases the stability of the compound, which means its shelf life is improved, and potency will remain the same for a more extended period. HHC is also more resistant than other cannabinoids to being stored improperly or exposed to UV light or heat.
Two enantiomers (pairs of compounds with precisely the same connectivity but opposite three-dimensional shapes) of HHC: 9α-HHC and 9β-HHC. The 9β-HHC enantiomer is much more active and could bind to CB1 receptors more readily than 9α-HHC.
Another related cannabinoid, HHC acetate (HHC-O), is up to 1.5 times more potent than HHC.
Download Our Free Guide to the ECS
Uses
HHC is said to cause a high similar to that caused by delta-9 THC; however, it is also said to have the sedating and relaxing properties of other compounds, such as delta-8 THC (which is nearly identical to delta-9).
HHC produces euphoric feelings and an alteration in visual and auditory perception, and it can also cause a change in cognition, heart rate, and body temperature. It is new to the market, so not many studies have examined HHC’s effects and potential for therapeutic use.
Potential Benefits
As HHC is structurally similar to THC, it could have anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, and anti-emetic effects. However, the main benefit of HHC lies in its stability as a compound due to its increased shelf life and stable potency. It is also thought to provide similar benefits to THC, including:
- Chronic pain management or relief, including neuropathic pain
- Decreasing symptoms of anxiety, depression, and insomnia
- Reducing inflammation
- Increasing sleep quality
- Decreasing vomiting or feelings of nausea
- Spasms associated with conditions like multiple sclerosis (MS)
- Cancer and the side effects of chemotherapy
Risks and Drawbacks
As HHC is an intoxicating compound, it can have some adverse effects similar to THC. This includes dizziness, dry mouth, red eyes, memory loss, anxiety, increased heart rate, coordination problems, and slower reaction times.
However, as HHC is less potent than THC, these side effects may not be as prominent. Other common side effects may include:
- Nausea
- Dry mouth
- Red Eyes
- Increased heart rate (tachycardia)
- Increase in appetite
- Anxiety
- Paranoia
- Insomnia and sleep disturbances
Synthetically-produced HHC, however, may have more severe side effects. This is because industrial processes often utilize harsh chemicals that can find their way into the final product.
Synthetically-produced HHC products are also likely to contain higher concentrations of HHC compared to natural cannabis so that higher doses may produce more severe adverse side effects.
Ultimately, more research is needed to determine the safety and efficacy of HHC.
Strains High in HHC
It can be challenging to find cannabis strains (cultivars) high in HHC specifically. However, cannabis cultivars high in THC may also contain higher HHC because as cannabis ages, THC degrades into HHC.
Some cultivars high in THC include:
- Bruce Banner
- Kush Mints
- Strawberry Cough
- White Rhino
- Gorilla Glue #4
What Is THC?
THC, or delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, is a cannabinoid molecule in cannabis. It is cannabis’s main psychoactive compound and causes the high that people experience when smoking marijuana. As delta-9 THC is from the plant, it is often called a phytocannabinoid.
Download Free Guide to THC
How It Works
THC binds to the body’s cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) within the nervous system and brain. It stays in the body for a long time, but the psychoactive effects wear off after a few hours.
Uses
THC is generally used for recreational purposes, but it also has several medicinal uses. For thousands of years, marijuana has been used to treat and alleviate symptoms of illness. It is often inhaled, ingested orally, applied as a topical ointment, or administered sublingually.
THC stimulates the release of dopamine from the brain, which causes feelings of euphoria. Its use can cause pleasant effects, and users may experience:
- Relaxation
- Increased sensory perception
- An altered perception of time
- Increased appetite
Potential Benefits
There are many potential therapeutic benefits of THC use, including aiding in the alleviation of ailments such as:
- Depression and anxiety
- Inflammation
- Insomnia
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and inflammatory bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)
- Migraines
- Nausea
- Pain
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Seizures
The FDA has even approved a synthetic THC medication called dronabinol to treat nausea and vomiting caused by chemotherapy, weight loss, and reduced appetite caused by HIV/AIDS.
Risks and Drawbacks
While THC use can give the user a pleasant experience, there are also potential adverse effects associated with its use. Some negative effects include:
- Anxiety
- Paranoia
- Coughing fits
- Chest and lung discomfort
- Fainting
- Cold sweats
- Hallucinations
THC use has also been associated with increased learning impairment and decreased memory formation, particularly among adolescents. Finally, marijuana is illegal under federal law. To use this cannabinoid, you need to live in a location that has legalized its recreational or medical use.
Similarities and Differences Between HHC and THC
THC and HHC are both intoxicating cannabinoids that produce a euphoric high for the user. The differences in THC and HHC come from their chemical structures: THC must be hydrogenated to produce HHC through a process that adds a hydrogen atom to the molecule, increasing its stability and resistance to heat and UV radiation.
How to Decide Which Is Best for You
When to Use HHC
Although people use HHC for medicinal and recreational purposes, there is no research to support specific use in any capacity. It’s essential to be careful about consuming synthetically-produced HHC products (or any synthetic cannabinoids) due to very little safety and regulation in this area. Ideally, it may be wise to avoid consuming them at all.
When to Use THC
THC can be used recreationally or medicinally. Many states have designated medical marijuana programs for their residents, allowing people to treat various medical conditions with THC. There are also therapeutic, synthetic THC products for medicinal use.
The Bottom Line
THC and HHC have very similar effects: Both produce feelings of euphoria and altered perception. HHC is still new to the market, so there has not been much research examining the short-term and long-term effects of the compound.
If you want a regulated product with some research to back it, regular THC (i.e., THC derived from marijuana) is the optimal choice. Apply for a medical marijuana card in your home state today to experience the many benefits of medical cannabis.
Get Your Medical Card
Connect with a licensed physician online in minutes.
Originally Published: February 2023
Last Updated: April 2024
Frequently Asked Questions
How strong is HHC compared to THC?
HHC is less potent than THC, resulting from the decreased binding affinity for the HHC molecule with CB1 receptors. When it comes to the high provided by HHC vs. delta-8 vs. delta-9 THC, users report that HHC “highs” feel somewhere between those from delta-8 and delta-9 THC.
How long does HHC high last?
Anecdotal reports suggest that HHC highs last around two to three hours.
Is HHC legal?
Like delta-8 THC, HHC is currently legal at the federal level thanks to the 2018 Farm Bill allowing the sale and consumption of hemp-derived products. However, some states have banned hemp products like HHC and delta-8, so be sure to check your local laws before consuming these substances.